Table of Contents
What are the Comorbidities of Obesity?
Obesity is a complex health condition that significantly increases the risk of various comorbidities, which are diseases or conditions that occur more frequently in people with obesity. Understanding these comorbidities is crucial for both prevention and effective management of obesity. Here are some of the most common comorbidities associated with obesity:
• Osteoarthritis: Excess weight puts additional stress on joints, leading to the degradation of cartilage and joint tissues, which can cause osteoarthritis, particularly in weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips.
• Sleep Apnea: Obesity is a major risk factor for sleep apnea, a condition characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. This occurs because excess fat around the neck can obstruct the airway.
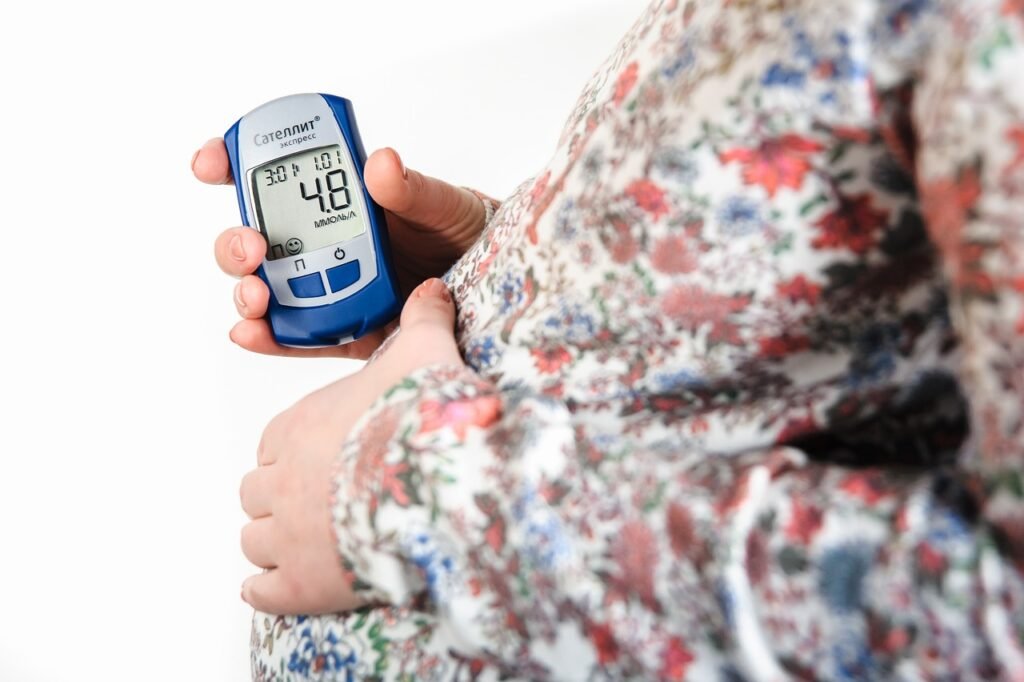
• Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity is closely linked to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels and eventually type 2 diabetes.
• Hypertension: Excess body weight increases the workload on the heart, leading to high blood pressure, or hypertension. This condition is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
• Heart Disease: Obesity contributes to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. The increased risk of heart disease is due to a combination of factors, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance.
• Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Obesity increases the likelihood of GERD, where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation.

What are the Effects of Obesity?
Obesity has widespread effects on the body, impacting nearly every organ system. Here are five key effects of obesity:
1. Respiratory Issues: Reduced lung capacity and obstructive sleep apnea are common among individuals with obesity. This can lead to chronic fatigue and decreased quality of life.
2. Musculoskeletal Problems: Excess weight strains bones and joints, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis and other musculoskeletal issues, leading to chronic pain and reduced mobility.
3. Reproductive Health: Obesity can disrupt menstrual cycles, reduce fertility, and increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, including gestational diabetes and preeclampsia.
4. Metabolic Syndrome: This cluster of conditions includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess body fat around the waist, all of which significantly increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
5. Mental Health: Obesity is linked to higher rates of depression, anxiety, and reduced quality of life, partly due to social stigma and body image issues.
How Does Obesity Affect Behavior?
Obesity can have a profound impact on behavior and daily life. The physical discomfort and health challenges associated with obesity often lead to decreased physical activity. Joint pain and fatigue can make exercise difficult, creating a cycle where inactivity leads to further weight gain. Eating habits are also affected; many individuals with obesity may engage in emotional eating or binge eating as a response to stress, depression, or anxiety. Social isolation is another significant issue, as stigma or reduced mobility can limit social interactions, further exacerbating mental health problems. Additionally, sleep disturbances, common in people with obesity, can affect mood and cognitive function, impacting daily behavior and overall quality of life.
What Happens When You’re Overweight?
Being overweight can have widespread effects on various body systems:
• Endocrine System: Hormonal imbalances, particularly related to insulin and sex hormones, can occur, leading to conditions such as insulin resistance and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
• Digestive System: Overweight individuals have a higher risk of developing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gallstones, and fatty liver disease.
• Musculoskeletal System: Excess weight puts additional strain on joints and bones, increasing the likelihood of pain and osteoarthritis.
• Cardiovascular System: The heart has to work harder to pump blood, leading to hypertension and an increased risk of heart disease.
• Respiratory System: Reduced lung function and a higher risk of respiratory infections and sleep apnea are common in people who are overweight.
Visceral fat, which accumulates around internal organs, is particularly harmful and is strongly linked to metabolic diseases.

What’s the Biggest Risk of Obesity?
The biggest risk of obesity is the increased likelihood of developing chronic diseases that can shorten life expectancy and reduce quality of life. The American Heart Association highlights that obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, which are the leading cause of death in the United States. Obesity also significantly raises the risk of type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and metabolic syndrome, further emphasizing the importance of addressing obesity to improve overall health outcomes.
What are the 4 Risks Overweight People Face?
Overweight individuals face several health risks, including:
1. Certain Cancers: Increased body fat is linked to a higher risk of several types of cancer, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer.
2. Type 2 Diabetes: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, contributes to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes.
3. Cardiovascular Diseases: Overweight individuals are at greater risk for heart attacks, strokes, and hypertension due to the added strain on the cardiovascular system.
4. Psychological Disorders: Depression, anxiety, and eating disorders are more common in overweight individuals due to body image issues and societal stigma.
How Does Obesity Affect Heart Health?
Obesity has a significant impact on heart health. Excess body fat requires the heart to work harder to pump blood throughout the body, leading to high blood pressure (hypertension). Additionally, obesity contributes to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. The American Heart Association identifies obesity as a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, underscoring the need for effective weight management to protect heart health.
What is the Link Between Obesity and Diabetes?
Obesity and type 2 diabetes are closely connected. Excess fat, particularly around the abdomen, leads to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This condition causes elevated blood glucose levels, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that about 90% of people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese, highlighting the strong link between these two conditions.
How to Avoid Obesity?
Preventing obesity involves adopting a lifestyle that balances energy intake and expenditure. Here are some tips to help avoid obesity:
• Behavioral Changes: Practice mindful eating, eat at regular times, and avoid eating late at night.
• Monitoring Weight: Regularly check weight and body measurements to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
• Education: Stay informed about nutrition and healthy lifestyles through credible sources such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and CDC.
• Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-fat foods.
• Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by the CDC.
What Doctors Consider are the Best Ways to Lose Weight?
Effective weight loss involves a combination of dietary, physical, and behavioral changes, with a focus on creating a caloric deficit. Regular exercise, including both aerobic and strength training, is crucial. A balanced diet prioritizing nutrient-dense foods while limiting empty calories is essential. Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help address emotional eating and develop healthy habits. In some cases, medical interventions like medications or surgical options such as bariatric surgery may be necessary.

What are the Common Reasons for Obesity?
Several factors contribute to obesity, including:
1. Lifestyle Choices: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and inadequate sleep.
2. Energy Imbalance: Consuming more calories than the body needs, leading to fat storage.
3. Metabolic Factors: Variations in metabolism can affect how efficiently the body burns calories.
4. Hormonal Imbalance: Conditions like hypothyroidism and PCOS can lead to weight gain.
5. Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and corticosteroids, can cause weight gain.
How can Public Health Policies Tackle Obesity?
Public health policies play a crucial role in tackling obesity. Here are a few initiatives:
• Education Campaigns: Raise awareness about healthy eating and physical activity.
• Food Advertising Regulation: Limit the marketing of unhealthy foods, especially to children.
• Access to Healthy Foods: Make healthy options affordable and accessible in schools and communities.
• Safe Environments: Build infrastructure that supports physical activity, such as parks and bike lanes.
• Healthcare Initiatives: Cover obesity prevention and treatment through insurance and community programs.
What is the Link Between Obesity and Mental Health?
Obesity and mental health are closely connected. Research shows that psychological distress can lead to emotional eating as a coping mechanism, contributing to weight gain. People with obesity are more likely to experience depression and anxiety due to societal stigma and discrimination. Negative self-perception and low self-esteem are common among individuals with obesity, further leading to mental health issues.
How Does Genetics Play a Role in Obesity?
Genetics plays a significant role in obesity. According to the CDC, if one or both parents are obese, their children are more likely to be obese due to genetic predispositions. Certain genes affect how the body stores and processes fat, appetite regulation, and energy expenditure, contributing to the development of obesity.
Can Diet Alone Reverse Obesity?
While diet is a crucial component, reversing obesity often requires a multi-faceted approach. Combining a healthy diet with regular exercise and behavioral changes is essential for effective weight management. In some cases, medical supervision may be needed to manage obesity. Engaging with support groups and healthcare professionals can significantly increase the chances of success.
What are the Best Physical Activities to Prevent Obesity?
The best physical activities to lose weight and prevent obesity include:
• Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, running, swimming, and cycling.
• Strength Training: Weight lifting, resistance bands, and bodyweight exercises.
• Flexibility and Balance: Practices like yoga and Pilates to improve overall fitness and prevent injuries.
How Does Socioeconomic Status Affect Obesity Rates?
Socioeconomic status (SES) significantly impacts obesity rates. Higher SES is associated with better knowledge of nutrition and health practices. Financial insecurity and stress related to lower SES can lead to poor food choices and lack of physical activity. Additionally, lower SES often means limited access to healthy foods, safe exercise environments, and healthcare, contributing to higher obesity rates.
What’s the Latest Research on Obesity?
Recent research has revealed new insights into obesity management:
• Pharmacotherapy: New medications targeting weight loss mechanisms are in development.
• Gut Microbiome: Studies show that the composition of gut bacteria affects weight and metabolism.
• Precision Medicine: Personalized approaches to obesity treatment based on genetic, metabolic, and behavioral factors are being explored.
How Do Cultural Factors Affect Obesity?
Cultural factors significantly impact obesity rates and management. Body image norms within different cultures can influence attitudes towards weight and health. Cultural norms and practices can either promote or hinder physical activity. Traditional diets and food cultures also affect nutritional intake and the prevalence of obesity.
What are the Common Diseases Related to Overweight and Obesity?
Obesity increases the risk of many diseases, including:
1. Liver Disease: Fatty liver disease and cirrhosis.
2. Certain Cancers: Increased risk of breast, colon, and endometrial cancer.
3. Heart Disease: Higher likelihood of coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
4. Type 2 Diabetes: Major risk factor due to insulin resistance.
Obesity is also associated with chronic inflammation, contributing to various diseases.
How Does Obesity Contribute to Weight Gain?
Obesity perpetuates weight gain through several mechanisms:
• Metabolism: Slows down, making it harder to burn calories.
• Hormones: Affects hormones like leptin and ghrelin, which regulate hunger and satiety.
• Physical Inactivity: Limits mobility and reduces physical activity.
• Psychological Factors: Stress, depression, and emotional eating add to calorie intake.
What is Excess Body Fat Related to Obesity or Overweight?
Excess body fat, especially visceral fat, is the hallmark of obesity and overweight. It accumulates due to:
• Poor Diet: High intake of calories, fat, and sugar.
• Lack of Exercise: Insufficient physical activity to burn calories.
• Genetic Factors: Family history and genetic predisposition to fat storage.
• Medical Conditions: Conditions like hypothyroidism and PCOS.
• Environmental Factors: Access to unhealthy food and lack of safe exercise spaces.
What are the Short-term and Long-term Effects of Obesity?
Short-term Risks:
• Fatigue: Low energy and tiredness.
• Joint Issues: Increased pressure on joints, leading to pain and arthritis.
• Breathing Problems: Sleep apnea and exacerbation of asthma.
Long-term Risks:
• Diabetes: Increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
• Cancer: Higher risk of breast, colon, and liver cancer.
• Heart Diseases: Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and hypertension.
• Mental Health: Higher rates of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
• Liver Disease: Risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and cirrhosis.
Understanding the broad impact of obesity on health is essential for effective prevention and treatment strategies.